Transforming data with dbt Core
Skypoint AI connects to your Git repository and runs your dbt models in your destination. Integrated with dbt Core, Skypoint AI allows you to use SQL queries to perform a wide range of data transformations, including aggregation, filtering, and data cleaning.
Prerequisite
You must fulfil the following prerequisites to proceed:
- An existing dbt repository.
- dbt models for data transformation.
Once you have defined your models, you can use the transformations in Skypoint AI Studio to run the SQL queries and create tables in your data warehouse.
If you don’t have an existing repository, Skypoint AI will create a repository for you in Azure DevOps.
To set up transformations
Follow the below steps to begin transforming your data via SQL:
- Go to Dataflow > Transformations.
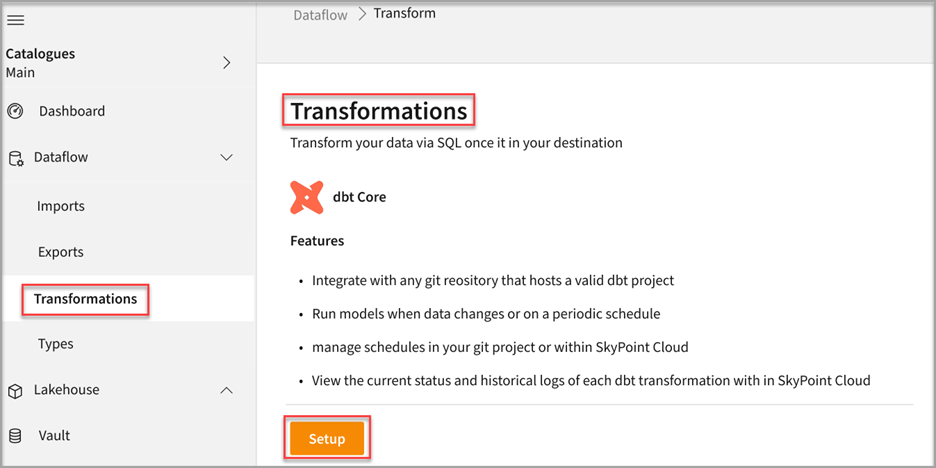
- Click Setup.
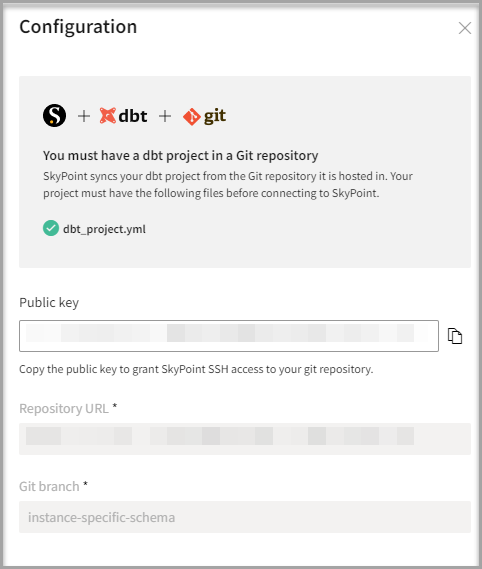
- On the Configuration page, find the public key and click the clipboard icon to copy it. You will need it to grant Skypoint SSH access to your Git repository.
Connect to the Git repository
You must have a dbt project in a Git repository. Follow the instructions for Git provider to grant Skypoint SSH access:
- For GitHub: See and follow the instructions for Managing deploy keys.
- For BitBucket: See and follow the instructions to Configure SSH and two-step verification.
- For GitLab: See and follow the instructions to Deploy keys.
Follow the below steps to validate credentials and connect with your Azure Git repository:
- Open your Git repository.
- In the User settings section, go to SSH public keys > New Key and paste the Skypoint AI public key in the Public Key Data field to synchronize your dbt project in the Git repository with Skypoint AI.
- On the Git repository main page, click Clone.
- Select the SSH command line and copy the repository URL.
Follow the below steps to verify the directory structure and define transformations in your dbt project:
- Navigate to your dbt project directory and open the
dbt\_project.ymlfile. You can define the directories of the dbt project and project configurations such as name, version, profile, etc. For example, themodel-pathssetting specifies the directories where dbt should look for model files.
model-paths: ["models"]
analysis-paths: ["analyses"]
test-paths: ["tests"]
seed-paths: ["seeds"]
macro-paths: ["macros"]
snapshot-paths: ["snapshots"]
- Open a
modeldirectory in your dbt project and define your data transformation models using SQL. Models are primarily written as aSELECTstatement and saved as a.sqlfile. For example, the{{config(materialized='table')}}directive in dbt is used to specify the materialization type table for a model.
{{ config(materialized='table') }}
with source_data as (
select 1 as id
union all
select null as id
)
select *
from source_data
Finish configuration
- Enter your Git Repository URL.
The repository location you specify should contain a model's directory from where dbt will look for your models by default. Once you have specified the location of your repository, you can create and maintain your dbt models within it. When you run transformations from Skypoint AI Studio, it will use the models in your repository to build your data model.
- Enter your Git branch.
The Connection tests pop-up appears.
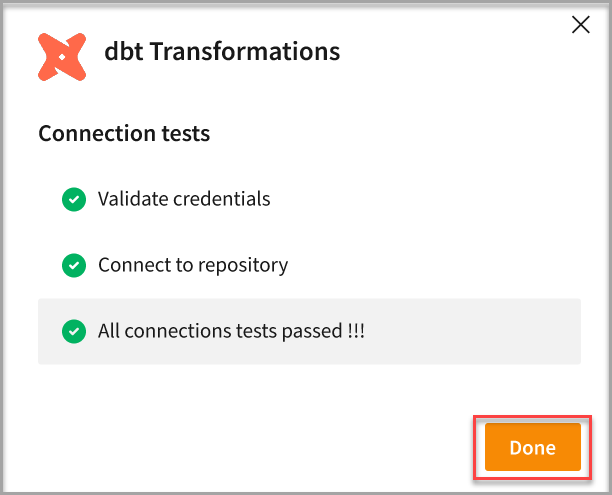
- Click Done.
- Once the sync with Git is completed, models from Git repo will get listed on the Transformations page.
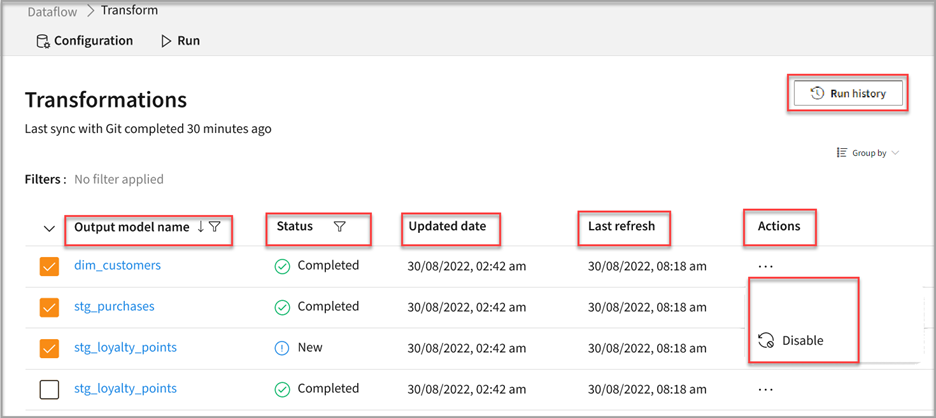
Run transformation models
- Go to Dataflow > Transformations.
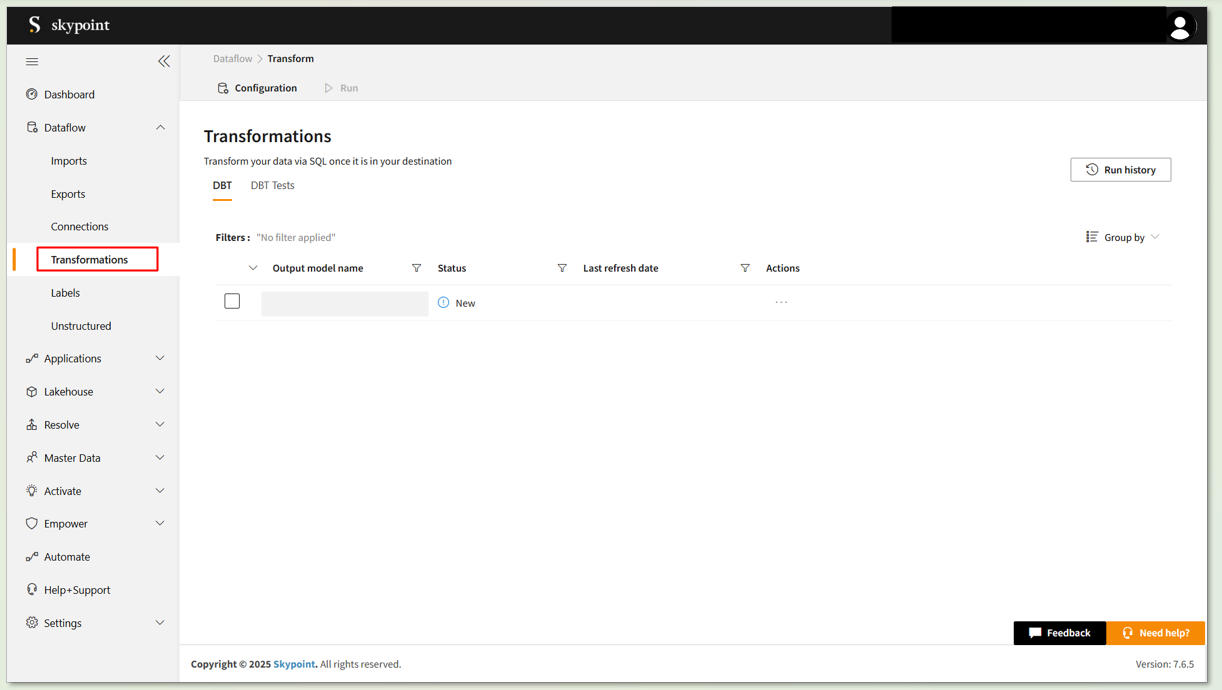
- Click Run to execute the desired Output model name.
- If you want to disable the dbt model, select your model and click Disable under the horizontal ellipsis in the Actions column.
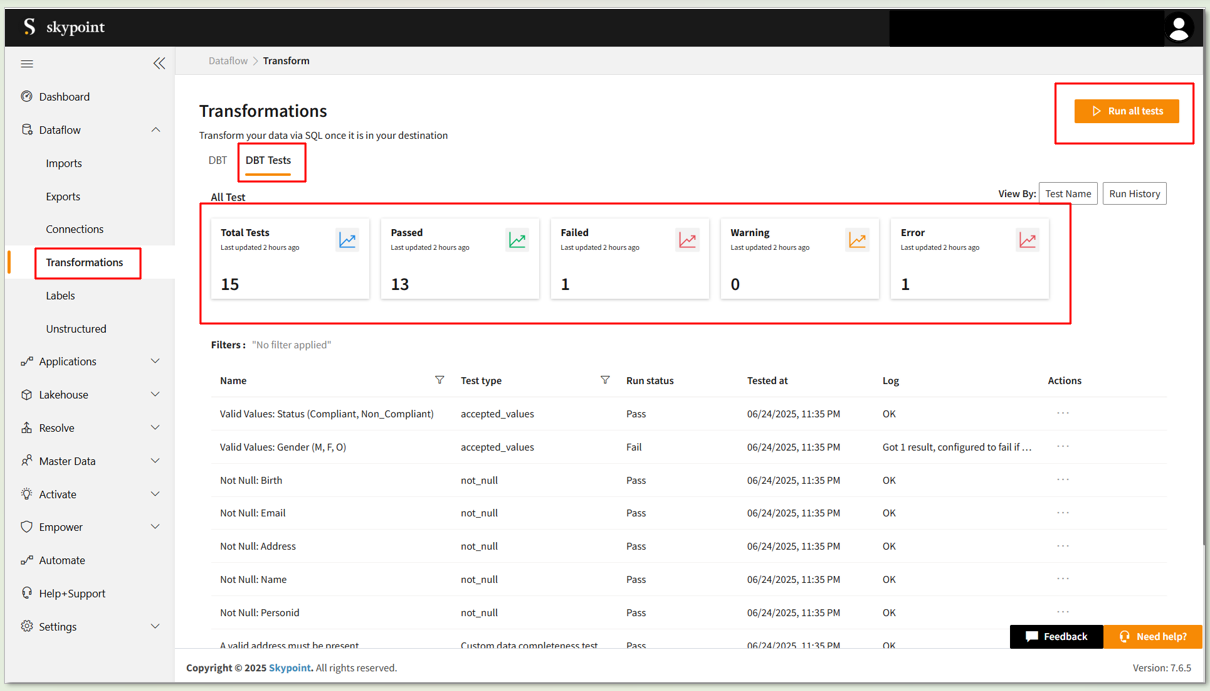
Click on the DBT Tests tab under the Transformations section to view all DBT test results, including totals, pass, fail status and detailed logs.
Click on the Run all tests button to execute all DBT tests.
Disabling a dbt model does not delete it from the system. It controls whether the record is available for use in transformations. You can always re-enable a disabled dbt model if needed.
- Select Run history to view all the states for transformation and the operation duration for the pipeline completion.
- Once the transformation is executed successfully, you can view the transformation tables in the Bronze tab under Lakehouse > Explorer.